Fatty Liver Disease Emerges as Silent Epidemic in India, Affecting Up to 50% Population
- bykrish rathore
- 17 January, 2026
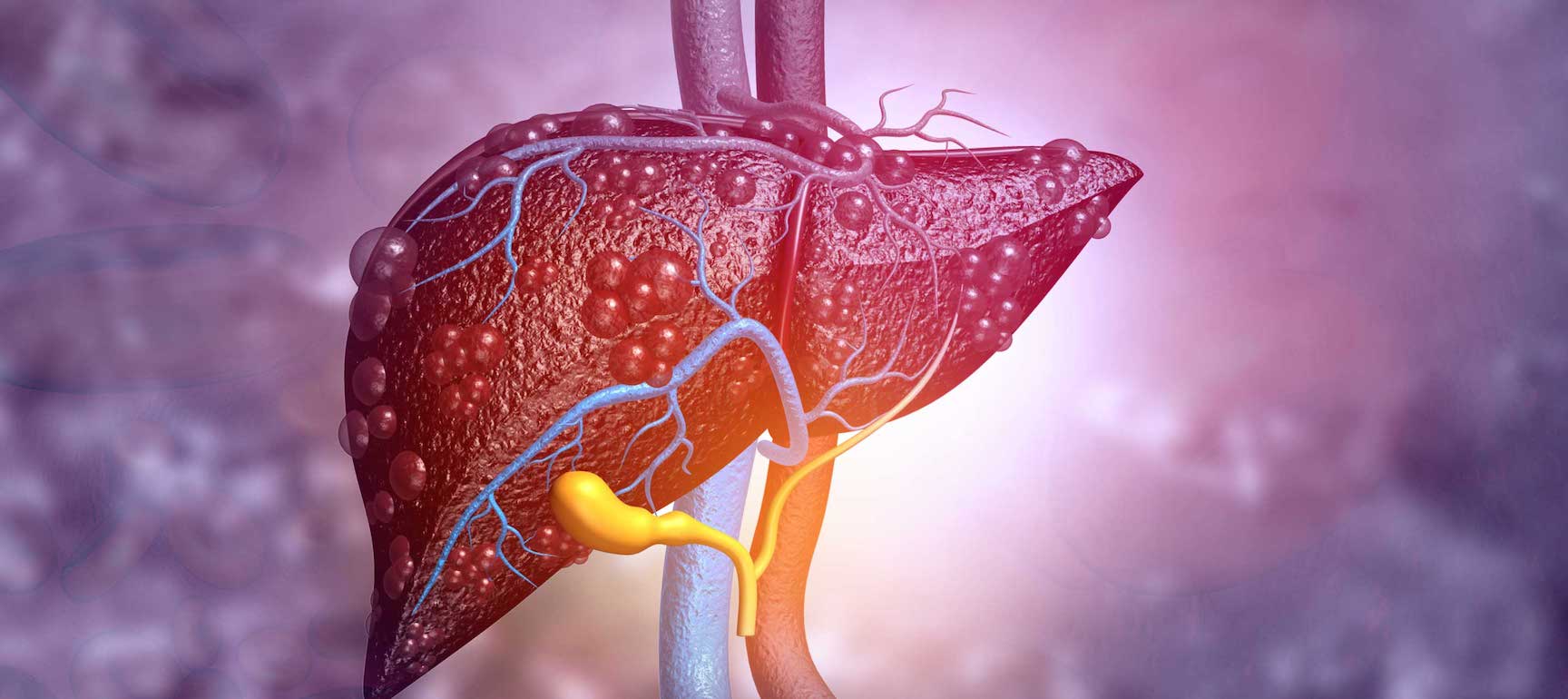
India is facing a growing public health challenge as fatty liver disease, now officially termed Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD), reaches alarming levels across the population. Once considered a condition affecting only a small segment of society, MASLD has now emerged as a silent epidemic, impacting an estimated 30–50% of Indians, according to medical experts and recent studies.
MASLD, previously known as Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), occurs when excess fat accumulates in the liver due to metabolic dysfunction rather than alcohol consumption. The condition is closely linked to obesity, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, insulin resistance, and sedentary lifestyles—all of which are on the rise in India due to rapid urbanisation and changing dietary habits.
One of the most concerning aspects of MASLD is that it often develops without noticeable symptoms in its early stages. Many individuals remain unaware they have fatty liver disease until it progresses to more severe forms such as steatohepatitis (inflammation of the liver), fibrosis, cirrhosis, or even liver cancer. This silent progression makes early diagnosis and prevention particularly challenging.
Doctors report that MASLD is no longer limited to older adults. Increasingly, young adults and even adolescents are being diagnosed with fatty liver disease, driven by poor diet choices, high intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and lack of physical activity. Alarmingly, non-obese individuals are also being affected, a condition often referred to as “lean fatty liver,” which is especially common in Asian populations.
The rising burden of MASLD poses serious implications for India’s healthcare system. Liver-related complications can significantly increase healthcare costs and reduce quality of life. Experts warn that if left unaddressed, MASLD could soon become one of the leading causes of liver transplants in the country.
Health professionals stress that early detection through routine health check-ups, including liver function tests and imaging, is critical. Unlike many other liver diseases, MASLD is largely preventable and reversible in its early stages through lifestyle modifications. Weight management, balanced nutrition, regular exercise, and control of blood sugar and cholesterol levels play a vital role in managing the condition.
Public health experts are calling for greater awareness campaigns to educate people about the risks of fatty liver disease and the importance of preventive healthcare. With India already battling high rates of diabetes and cardiovascular disease, addressing MASLD is essential to preventing a wider metabolic health crisis.
As India’s lifestyle patterns continue to evolve, tackling this silent liver epidemic will require coordinated efforts from individuals, healthcare providers, and policymakers to promote healthier living and reduce the long-term burden of liver disease.

Note: Content and images are for informational use only. For any concerns, contact us at info@rajasthaninews.com.
40 के बाद शर्ट से बा...
Related Post
Hot Categories
Recent News
Daily Newsletter
Get all the top stories from Blogs to keep track.





_1772465804.jpg)
_1772465408.jpg)
_1772464394.jpg)